Nerve cell
Neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It consists of three parts-
1. Dendrites: Dendrites are branched cytoplasmic projections from the cell body. The dendritic tip of the nerve cells receive impulses and sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse which is further transmitted to the cell body.
2. The cell body: The cell body contains a well defined nucleus, surrounded by cytoplasm. It has cell organelles like any other cells. The cell body further transmits the impulse to the axon.
3. Axon: One branch arising out of the cell body is very long in comparison to others. This branch is called axon or nerve fibre.
1. Dendrites: Dendrites are branched cytoplasmic projections from the cell body. The dendritic tip of the nerve cells receive impulses and sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse which is further transmitted to the cell body.
2. The cell body: The cell body contains a well defined nucleus, surrounded by cytoplasm. It has cell organelles like any other cells. The cell body further transmits the impulse to the axon.
3. Axon: One branch arising out of the cell body is very long in comparison to others. This branch is called axon or nerve fibre.
Transmission of the nerve impulse
- It means flow of message through the nerve. Nerve impulse upon generation passes along a neuron in only one direction.
1. Through the synapse the impulse passes from one neuron to the next neuron.
2. When an impulse reaches the end of first neuron, a neurotransmitter is released in the synaptic cleft of the synapse.
3. These chemicals cross the gap or synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in the next neuron.
Plant hormones
There are four types of plant hormone. They are as follows:
- Auxins- Involved in differentiation of vascular tissue, control cellular elongation, prevention of abscission, involved in apical dominance and various tropisms, stimulate the release of ethylene, enhance fruit development
- Cytokinins- Affect cell division, delay senescence, activate dormant buds.
- Gibberellins- Initiate mobilization of storage materials in seeds during germination, cause elongation of stems, stimulate bolting in biennials, stimulate pollen tube growth.
- Abscisic acid- Maintains dormancy in seeds and buds, stimulates the closing of stomata.
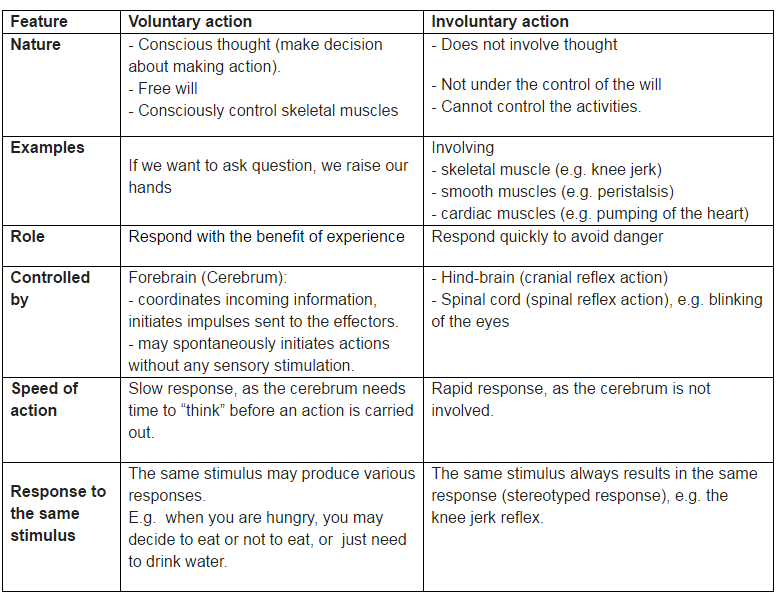
Reflex action
- There are certain actions in our body that are spontaneous and do not need any processing by the brain. Such actions or responses are called reflex actions.
- Reflex actions are involuntary actions that occur without conscious thought processes.
- For example, when some particles fall into your eye, there is immediate flushing of tears to wash them out (glandular secretion).

No comments:
Post a Comment